Catena Core
Catena Core is like the engine of Catena. It creates a consistent framework to operate and develop services, a core set of components and behaviors services can leverage for common tasks, and its extensible design means it can be molded to support new features without re-architecting.
Catena node architecture
A Catena node consists of a set of components and built-in functionality along with a set of services and each of their dependencies.
The Catena node defines some common, low-level interactions, protocols, and expectations. For example:
- Session-based or API-key-based authorization
- Catena services are typically gRPC services and this is well-supported
- Databases can implement a common config framework and migrations can be handled automatically
- A session store will be made available when required
- There will be a way to resolve platform accounts when required
- Services may include a standard heath-check that can be leveraged at the node level
There are components and capabilities of a Catena node that are always available and services can expect to leverage these. Other components are swappable or optional. This allows a node to be extended to support new platforms/providers or to minimize its footprint.
Depending on the context, "Catena node" is used to refer to both a process running a set of Catena services and the core set of functionality that runs and provides capabilities to the services.
Swappable components
There are node-level swappable components, such as the audit log, but services may also depend on components that can be swapped or customized. Those components can then have their own swappable dependencies. Catena does not limit the depth of customization which when customization is necessary the scope of the change can stay focussed, allowing faster, more consistent development.
For example, while the matchmaking service provides a consistent interface to game clients, the matchmaker running inside the service can be swapped or replaced with a custom implementation. This allows significant reuse of existing functionality and a narrow scope of customization when necessary. (The Catena Matchmaker even has things about it such as matchmaking strategies and data-handling hooks that can be further customized without replacing the whole matchmaker.)
Node building and running
At startup, the Catena process handles the building (runtime configuration) of a node based on configuration files, environment variables, the available services and components, their required dependencies. It will process any database migrations and check to make sure each service can start. Once it is running, it will handle the rest of the node lifecycle, request routing, authorization, and logging.
Catena supports loading services/modules/components from other libraries - they do not need to exist within the Catena code tree. This allows for easy creation and sharing of custom modules by anyone.
Catena node diagram
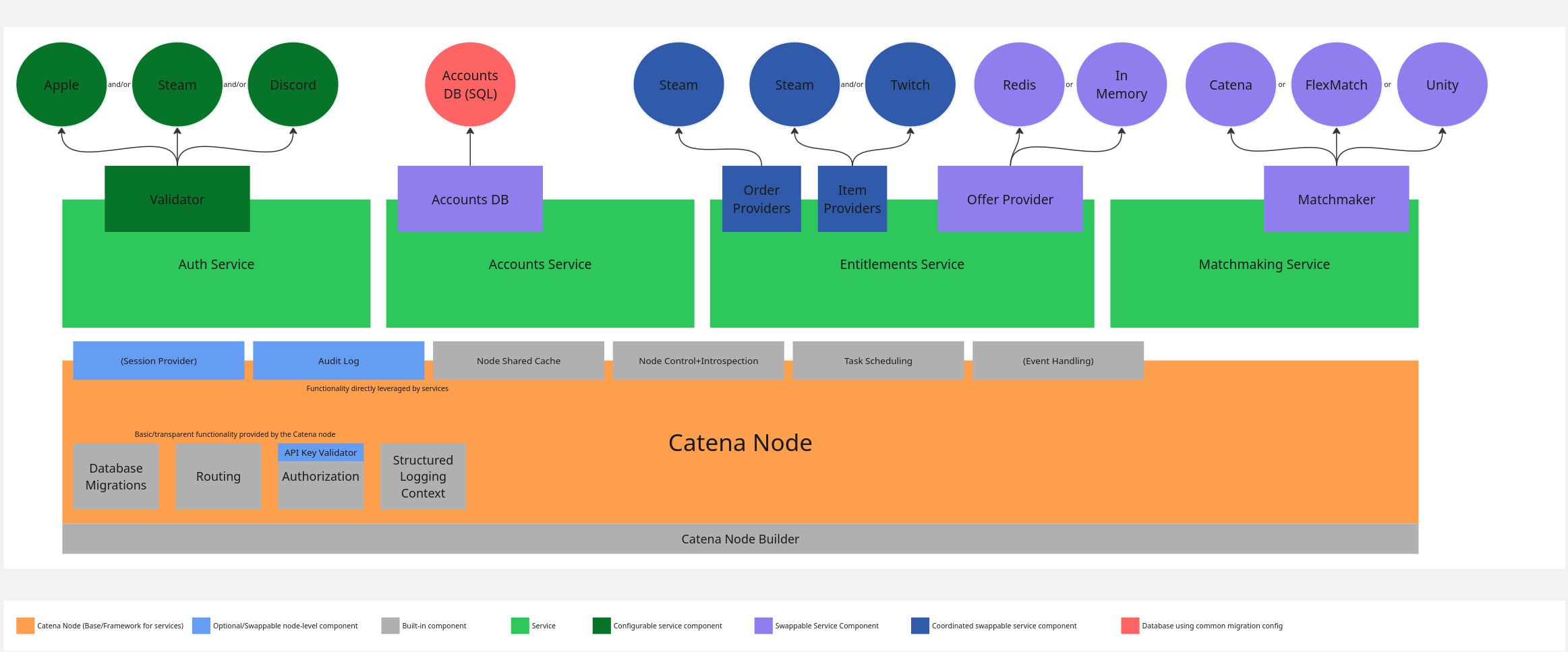
For a bigger image, right click and "Open Image in New Tab"
This is not an exhaustive diagram; it illustrates the layers different components exist at in Catena and whether they are swappable.
Terms:
- A "swappable" component is one where a custom implementation may be written and the node/service can leverage it immediately.
- A "coordinated swappable" component is similar but the service must have some small logic added to identify the custom implementation.
- A "configurable" component is one where new implementations may be written and the service can leverage it along with others (enable/disable or choose only 1, service dependent).